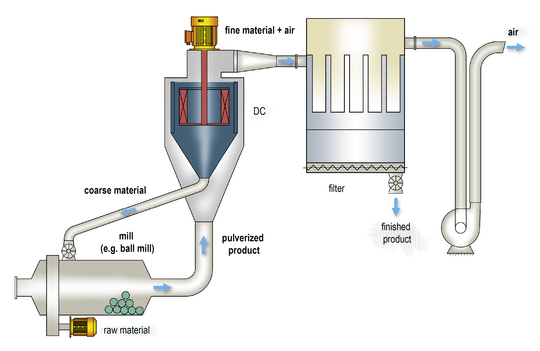
The feed material is fed to the classifier from below with the process air. The deflector ring in the classifier enables the product to be fed to the classifier wheel from above. Simultaneously, the process air flows radially into the classifier wheel. Uniform classification conditions and the use of the entire classifying zone enable maximum yields with minimum energy requirements.
The deflector classifier is not only suitable for combination with new systems. It also improves the quantity produced and product quality for existing systems such as ball mills and micronizers which are equipped with older construction style classifiers.
The increased efficiency of the classification process relieves the upstream mill. Thus, the mill can crush more material with reduced specific energy requirements. At the same time, product quality is increased due to a more precise upper grain restriction.
